Gears are used in many kinds of machines. These rotating circular parts have cut or inlaid teeth, such as gear wheels, that mesh with another toothed part to provide torque. The teeth of two mating gears are the same size. You can use gears to change the rotational speed, torque, and direction of power transmission.
Have you ever thought about how gears are manufactured?
Hobbing is the procedure by which gears are widely made nowadays. This method is used to make spur and helical gears. It is the recommended method because hobbing is both fast and cost-effective.
What is Hobbing?
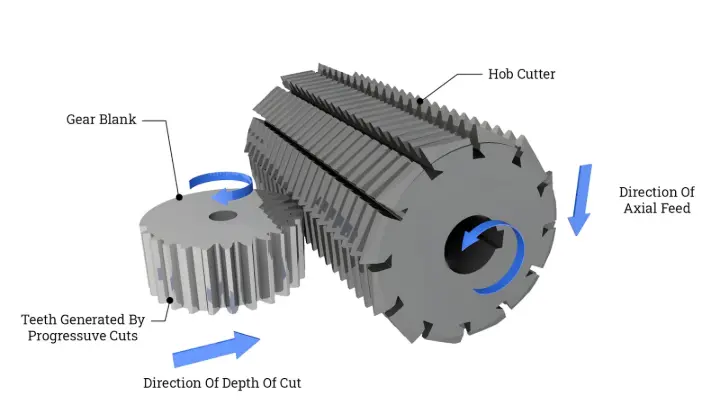
Hobbing is the machining procedure used to cut gears on a machine. Hobbing machines are a unique type of milling machine. The gear teeth are gradually carved into the base material using a cutting tool called a hob.
This method of gear manufacturing is less expensive than other processes and is also highly accurate. For this reason, hobbing is widely used in gear production.
Hobbing machines have two oblique spindles, one attached to the workpiece and the other to the hob. The required angle between the hob and the workpiece changes depending on the gear being produced.
Rotating the shafts at a fixed ratio results in the desired number of teeth on the workpiece. The hob is then inserted into the workpiece until the proper tooth depth is reached.
Hobbing machines (also called hobbers) come in different sizes. These are fully automated machines capable of producing a wide variety of products, including small-sized gears to industrial-sized gears.
Types of Gears Made By Hobbing
Helical gears — Helical gears, often called "dry fixed gears," provide a certain level of precision. This is possible because the leading edges of the teeth are not parallel to the axis of rotation. The shape of the teeth of helical gears represents a helix section. These are the recommended solutions for machines with high speeds or loads.
Sprockets — Sprockets are shaped wheels with teeth or cogs. They can be coupled to a track or chain that runs through them. They differ from normal gears in that the sprockets are not directly connected to each other. Sprockets are commonly used in bicycles, motorcycles, and automobiles, as well as other devices that require rotational motion between two shafts.
Involute Gears — Involute gears are one of the most common gear options today, as their tooth design allows for seamless power transmission with minimal speed or torque required. Gears used in high-power applications are typically helical involute gears, which have spirals of different hands and rotate in opposite directions.
Ratchets — Ratchets provide continuous linear or rotational motion in one direction only. They are used in situations where it is necessary to prevent movement in the other direction. Ratchets consist of a circular gear with teeth and a rotating, spring-loaded finger called a pawl. They are used in a variety of applications, including tools, slacklines, shackles, and cable ties.
Spur Gears — Spur gears can also be made by hobbing. These are the most basic type of gear, consisting of a cylinder or disk with radially spaced teeth. These gears can mesh effectively only when connected to parallel shafts. The weight of the teeth does not produce any axial thrust. They are ideal for use at low speeds, but can be extremely noisy at high speeds. They are widely used in machinery to increase or decrease speed.
Splines — Mechanical splines are teeth on a drive shaft that engage with grooves to transfer torque and maintain angular consistency. Their most common use is in automobile drive shafts, which transmit torque and rotation.
Worm gear — Worm in this context means a screw-shaped gear. These are also called "endless screws" and are used to slow down rotational speed or transmit more torque. Their main advantage is that they can transmit motion in 90 degrees. The worm in a worm gear may have single or multiple starts, and each 360-degree rotation of a start advances the gear one tooth. They serve as tuning mechanisms for guitars, roller cotton gins, and other musical instruments.
What is a Gear Hobbing Cutter?
A hob is a cutting tool used to create teeth in a blank workpiece by hobbing. Hobs with a cylindrical design are equipped with annular cutting edges and continuous grooves along their length.
These teeth help in cutting and removing chips. Special hobs are also made for specific products, such as sprocket gears.
The cross-sectional shape of the hob teeth is approximately equal to the teeth of the rack gear that will be used in the finished product.
These small changes in the cross-sectional shape are only necessary for cutting, but each tooth of the hob is slanted from the back side to reduce friction.
Although hobs are usually designed with a single thread, multiple-thread options are used at times to improve productivity. The only drawback is that they can be less accurate than single-thread hobs.
Both general-purpose and custom-made hobs are used, depending on the scope of the project. Custom hobs for a specific job vary because they are used to make gears with altered tooth profiles.
Benefits of Gear Hobbing
Gear hobbing service has helped OEMs in many ways. The following are some of the significant benefits of this method:
- Gear hobbing is faster and effiecient than any other gear producing techniques. Plus, the machines are easy to use and don’t need much attention during operation.
- CNC gear hobbing machines are used to cut gears into the workpiece. It offers accuracy that no other machine can match. It works in a nearly automatic mode, and the computer program for the design and process helps to reduce human errors and produce high-quality, performance-driven gears in large quantities.
- A wide range of gears suitable for various purposes can be produced with this method. Gear hobbing allows any number of teeth to be produced while maintaining high quality.
Conclusion:
Because gear hobbing is quick, precise, and efficient, it has become the industry standard for producing a wide variety of gears. This method allows for the mass manufacture of complex helical and worm gears as well as basic spur gears without compromising quality. The possibilities of this technology are further improved by CNC gear hobbing machines, which make it highly automated and reliable for contemporary manufacturing needs. Gear hobbing remains a vital solution for producing precise and long-lasting gears for a wide variety of applications as industries continue to require high-performance components.